From April 9-10, Harker hosted the 15th annual Research Symposium, inviting the Harker community to experience the breadth of its research opportunities by viewing student presentations and hearing keynote speakers deliver fascinating talks on the theme of this year’s event: artificial intelligence, robotics and automation. The 2020 symposium was canceled due to safety concerns caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
This year’s symposium was held virtually with all presentations, keynote talks and exhibitions delivered via Zoom, requiring impressive coordination between event organizers, presenters and technology staff.
Throughout the two-day event, middle and upper school students delivered poster presentations on research they had conducted on topics such as environmental science, physics, astronomy and medicine. The presentations were held in special breakout rooms, with plenty of time scheduled for each speaker. Corporate exhibitors – which included Microsoft, NVidia, Oculus and ZeroUI – each received their own room that visitors could drop into at their leisure, mimicking the atmosphere of the exhibition area in previous years.
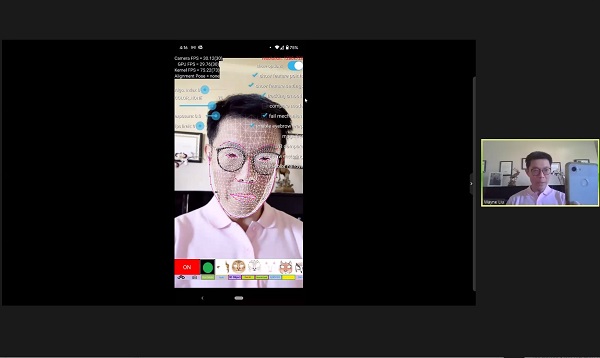
The event kicked off on Friday with Wayne Liu of Perfect Corp, whose app YouCam Makeup allows users to demo beauty products using artificial intelligence and augmented reality technology, and was named one of Time Magazine’s best innovations of 2020. Liu provided an overview of the history of artificial intelligence and how it developed into the technology used by YouCam Makeup. “Facial recognition is not new,” he said, “However, to get to the point where you can [try on makeup virtually] … the technology needs to be very precise.” To achieve this precision, Perfect Corp gathered and analyzed millions of hair color and skin tone samples, and their app uses 3,900 polygon meshes to achieve accurate results.
Dr. Ben Chung, associate professor of urology at Stanford’s School of Medicine, provided an overview of robotics-enabled surgery and how it has been used to make certain very difficult procedures much easier and safer, such as the removal of prostate cancer. He also showed footage of his own procedures using surgical robots in which he removed a tumor from a kidney. “Where the robotic platform really helps us is the ease of the suture,” he said. “Making sure that your suturing is exact is really important because you need to make sure that the patient doesn’t bleed afterwards.” As the technology of robotic surgery evolves, Dr. Chung said, it will be applicable to more situations, such as conducting surgery over long distances in situations such as on a battlefield or in a space station.
Any discussion of artificial intelligence and robotics invariably touches on the legal and ethical aspects of these fields, and Ryan Calo’s presentation on legal rulings on the use of robots was a great forum for the topic. Calo, a law professor at the University of Washington, explained that “robots have been with us for a very long and so we shouldn’t really be surprised that occasionally they have led to legal disputes.” These disputes extend as far back as the 1880s, when it was questioned whether using artificial wooden coins in vending machines constituted fraud. In the 1950s, courts found that robots could not be defined as dolls because they were not representations of human beings and thus could not be subjected to the same tariffs. Present day debates have centered on the ownership of artifacts retrieved by robots from shipwrecks and how to prosecute crimes in which machines are used to steal from homes.
Fitting for the symposium’s 15th anniversary, this year’s alumni keynote was delivered by Yi Sun ‘06, who 15 years ago was Harker’s first Science Talent Search finalist and a member of Harker’s first US Math Olympiad team, winning a silver medal. In his talk Sun, who now works as an assistant professor at the University of Chicago’s department of statistics, explained the process of how machine learning tasks often involve discerning signals from “noisy observations.” Using detailed diagrams, Sun discussed the mathematical concepts underlying the problem and how they are used to process data for electron microscopy.
The final keynote speaker for this year was Chelsea Finn, assistant professor in computer science at Stanford University, who presented on the process of teaching robots how to learn and solve problems the way humans do. Finn noted that while it was possible to teach robots to do certain tasks – such as piecing together a toy airplane or place shapes into a cube – through trial and error, these robots became highly specialized due to gathering data from very controlled environments using specific tools. Teaching robots how to perform “simpler, but broader” tasks with a greater range of applications is much more difficult, and Finn explained the methods she and her team have used to create robot “generalists.”